There is a rapid pace of transformation occurring within the healthcare industry, driven by the growing mobile app market. In a few short years, mHealth has gone from an upstart industry to one that’s projected to reach 50 billion U.S dollars in 2025—way above 2016 figures. With 89% of U.S. adults and 78% of adults worldwide owning smartphones, the use of these devices makes healthcare more equitable and accessible, especially in communities with limited medical resources.
In the coming years, the standards for virtual care are expected to converge with those of in-person care, with a growing emphasis on quality and safety. As of November 2022, the Food and Drug Administration has been accelerating approvals of medical artificial intelligence tools, authorizing more than 520 devices.
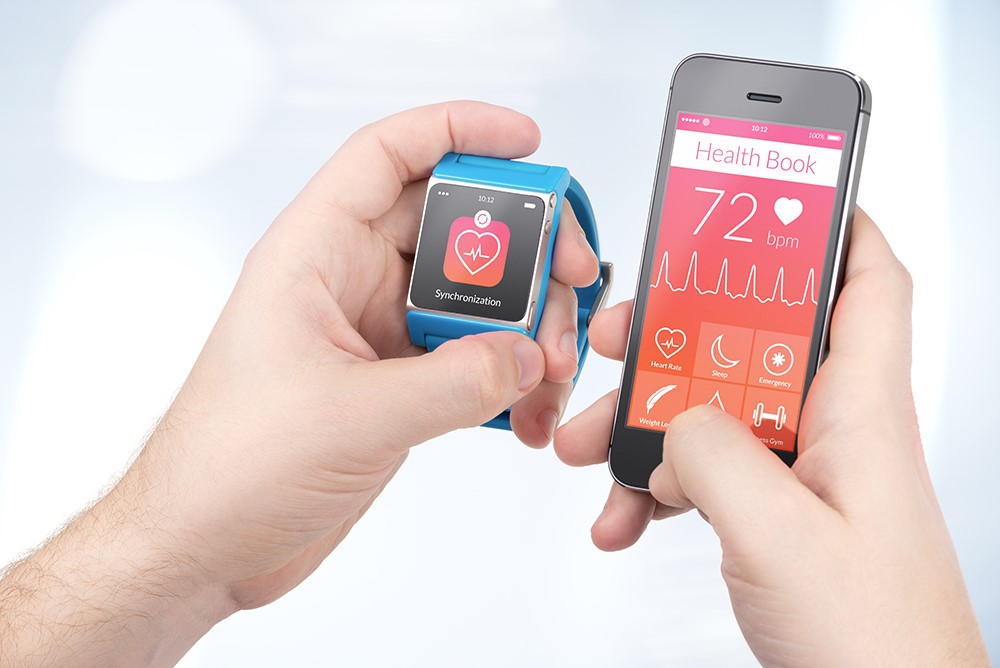
All this led to the emergence of the new term “quantified self” – the phenomenon of individuals beginning to track their various health indicators, including behavioral, physiological, biological, and others. By adopting mHealth apps, patients increased their levels of exercise, consumed healthier low-calorie food, took more steps, and improved their sleeping habits. Moreover, tailored app notifications were found to be more successful in reducing visits to the doctor’s office and shifting towards telemedicine.
Benefits of Mobile Health Apps
Let’s take a closer look at several benefits of mobile health application bring to the table:
- Remote access. The use of mHealth apps empowers patients to easily reach experts, regardless of their location, at any time of the day or night. In turn, doctors have access to required health information, including blood pressure and other vital indicators, as well as sharing important healthcare resources.
- Communication without barriers. Mobile health apps for patients enable appointment management, ensure timely reminders, and provide a secure messaging system.
- Adherence to prescribed treatments. Those in need can stay on track with their treatment plans and receive regular follow-ups from their physicians.
- Self-management. These platforms can motivate patients to stay consistent and conscious of their lifestyle and wellness which can contribute to improved management of chronic conditions. Apple has set an example by partnering with Medicare plan providers to lower the cost of its watches for the elderly through subsidies.
The combination of mobile applications in healthcare with other market trends like virtual reality (VR)/augmented reality (AR) technologies, data analytics solutions, wearable Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and blockchains drive the change. For example, by utilizing AR-enhanced images, patients can use their device’s camera to view a high definition version of a body part or medical procedure, such as a brain scan or MRI, in 3D from any angle. VR applications work within immersive platforms to simulate treatment sessions without actually being present at the clinic, reducing costs for visits, tests, and patient anxiety around unfamiliar locations.
Wearable IoT devices gather information in real-time, making it easy to monitor and alert patients when key health factors change. With AI-driven analytics, data collected from these devices can be processed quickly and used to create more precise treatments tailored to a patient’s individual needs.
Blockchain fuels healthcare supply chain management by tracking each product from its source up until delivery; nothing gets lost or misplaced and no money is wasted on expensive or unnecessary inventories. Security measures such as biometric screening ensure limited access to patient’s medical data.
Considering the numerous solutions available, how do you differentiate your solution in today’s competitive market? Creating a relevant and effective mobile health solution can be a tricky endeavor as the outcome heavily relies upon the organization’s goals and investment. Before launching the development process you need to take into account: data security, user experience, integration of third-party apps, scalability, and regulatory compliance. At the very beginning of the tailored mHealth app development, understanding the key needs of the target audience can become a cornerstone of the project’s future. It is also essential to properly research additional challenges that can arise, such as lack of interoperability and fragmentation between different devices, operating systems, and mobile platforms.
Bottom Line
The mHealth market growth is attributed not just to advances in technology and popularity of fitness apps, but also to increased patient awareness, convenience, and a change in physician preference. Furthermore, healthcare practitioners are increasingly making use of AI-powered medical tools for accelerating prescription decisions – leading to better patient outcomes and decreased number of hospital visits. Also, advanced wearable IoT devices that ‘quantify’ users’ lives, enables people to receive more holistic nutrition programming, effective lifestyle coaching and focused health plan management. This has resulted in increased awareness about personal health needs among various demographics worldwide transforming how we interact with our wellness today.

0 Comments