Psoriasis is a long-term skin condition affecting millions of individuals worldwide. It leads to the development of uncomfortable red, itchy, and scaly patches on the skin. While a complete cure for this condition is unknown, treatments are available to manage its symptoms and enhance the quality of life.
This blog post will delve into the reasons behind psoriasis’s symptoms and the various treatment options. The aim is to provide an understanding of this condition.
Certain factors like genetics, stress levels, and infections can cause psoriasis. These include;
Genetics
Genetics plays a role in determining one’s susceptibility to psoriasis. Research has indicated that individuals with a family history of psoriasis are more prone to developing this condition than those without a history. Several genetic mutations have been identified in people with psoriasis, including gene variations for regulating responses, skin cell differentiation processes, and inflammation. However, it’s important to note that not everyone with a family history of psoriasis will necessarily develop the condition themselves. Similarly, not everyone affected by psoriasis has a background associated with it.
Immune System Malfunctions
Psoriasis is often described as a disorder indicating that the immune system mistakenly targets cells in the body, causing inflammation and excessive growth of skin cells. Studies have revealed that specific immune cells, such as T cells and dendritic cells, play a role in initiating and maintaining psoriasis. T cells are components of our responses responsible for identifying and fighting off foreign substances like bacteria or viruses. However, in psoriasis, these T cells erroneously attack skin cells instead, resulting in inflammation and rapid skin cell multiplication.
Triggers from the Environment
Environmental factors can contribute to flare-ups of psoriasis. These include stress, infections, injuries to the skin, and cold weather conditions. Stress is widely recognized as a trigger for psoriasis, and managing stress levels can help alleviate symptoms for some individuals. Skin injuries or infections like cuts or streptococcal infections can act as triggers or exacerbate existing symptoms of psoriasis. Additionally, exposure to weather conditions can cause dryness and flakiness of the skin while worsening psoriasis symptoms.
Impact of Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle habits may also aggravate psoriasis. Smoking has been associated with an increased risk of developing psoriasis. It can worsen symptoms in individuals already affected by this condition. Consuming a rich diet in sugar-processed foods and red meat has also been discovered to promote inflammation within the body. This inflammation can potentially exacerbate the symptoms of psoriasis. Furthermore, drinking alcohol while taking medications for psoriasis can disrupt their effectiveness. Heighten the likelihood of experiencing side effects.
Medications and Treatment
Some medications and treatment options for other conditions can also trigger psoriasis in some people. These medications include beta-blockers, lithium, and antimalarial drugs. However, this is relatively rare, and most people with psoriasis don’t develop the condition as a side effect of medication. Conversely, numerous treatment options can help manage psoriasis symptoms, including topical creams, medications, light therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
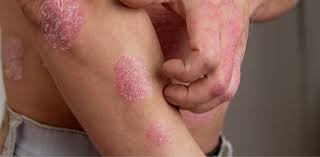
1. Red and Itchy Patches: Psoriasis often causes red and itchy patches to appear on the skin, especially on the knees, elbows, scalp, and lower back. These patches may be small or large, usually silvery or white in color. The patches may also be inflamed, swollen, and painful.
2. Thickened Skin: The skin can become very thick and scaly in psoriasis. This can cause difficult movements and may lead to joint pain or stiffness. The thickened skin can also result in cracking and bleeding in severe cases.
3. Nail Changes: Psoriasis can also cause changes in the nails. They can become thick, yellow, or brown and detach from the nail bed. Nail psoriasis can cause discomfort and can be challenging to treat.
4. Scalp Psoriasis: This type of psoriasis involves patches on the scalp, causing silvery-white scales on top of the head. It can be itchy and uncomfortable and can result in hair loss. Scalp psoriasis can also lead to flakes falling from the head onto clothing and other surfaces.
5. Joint Pain: Approximately 30% of psoriasis patients develop psoriatic arthritis, a type of arthritis that causes painful, inflamed joints. Psoriatic arthritis can occur at any time, with or without skin symptoms.
What is the Best Treatment for Psoriasis?
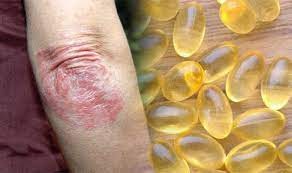
There are options for treating psoriasis ranging from fish oil for psoriasis, creams, and ointments that can be bought without a prescription to medications and light therapy that require a prescription. Topical treatments like corticosteroids and vitamin D analogues reduce inflammation and relieve itching.
Oral medications such as antihistamine for psoriasis, methotrexate, and cyclosporine suppress the system and alleviate symptoms. In some cases, doctors may recommend light therapy or phototherapy, which involves exposing the skin to light to reduce inflammation.
Aside from treatment, lifestyle changes can help manage psoriasis symptoms effectively. Avoiding triggers like stress, smoking, and alcohol can significantly minimize flare-ups. Adopting a diet and maintaining exercise routines are equally important as they contribute to overall well-being while reducing inflammation in the body.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a long-term condition that can be challenging to handle, but treatment methods and lifestyle adjustments can improve symptoms and lead a fulfilling life. If you suspect you may have psoriasis, consult with a healthcare professional for a diagnosis and discuss your treatment options. Remember that psoriasis is manageable, and there is support for you.
0 Comments